Table of Contents
Introduction
“Server DNS Address Could Not Be Found” error occurs when the Domain Name Server (DNS) cannot determine the website’s IP address. When you visit a website, the browser’s initial action is to contact the DNS server, but this DNS lookup might sometimes fail, resulting in an error. Yes, you will not be able to access any websites until the problem is rectified. This is what the error looks like:
This site can’t be reached
xyz.com’s server DNS address could not be found
Try:
- Checking the connection
- Checking the proxy, firewall, and DNS configuration
- Running Connectivity Diagnostics
ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED
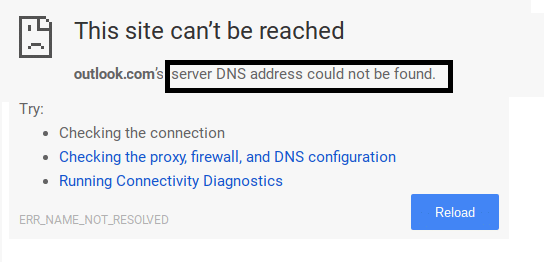
As you can see, this issue has a lot of information and a few pretty helpful troubleshooting techniques.
Pre Fixing Steps
Following the previous steps seemed to solve the problem in most cases, so we’ll go through them again. However, before moving ahead, check for the following:
Reboot Your System
Sometimes rebooting your system helps quite a lot in many things. It sets some of your settings to the default and gets rid of the issue.
Check for the Connectivity
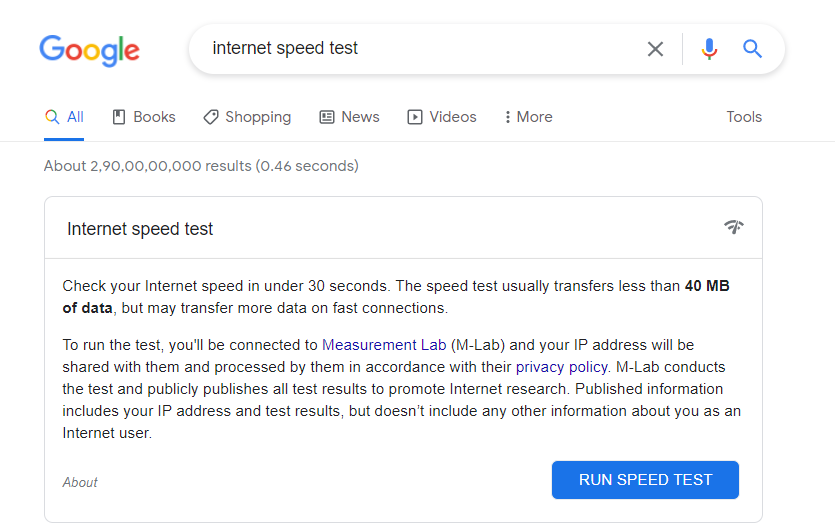
Check if your internet is working fine. In order to check the speed of the internet, you can open Google and take the internet speed test. If the speed does not match your requirement, you can switch your networks.
Remove Unnecessary Chrome Extensions
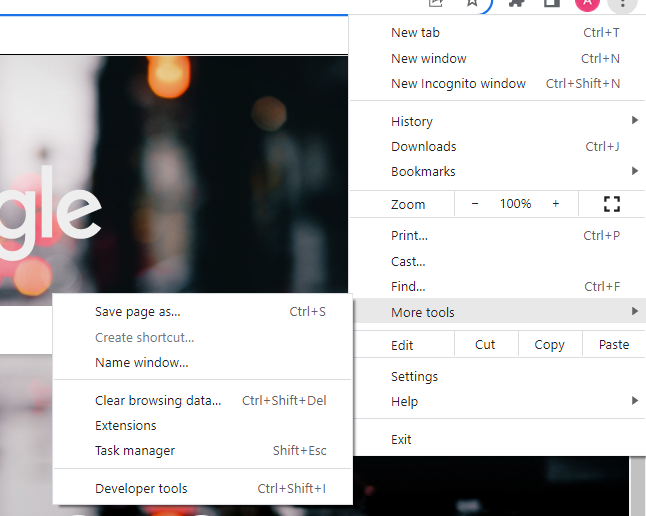
Step 1: More Tools can be found by clicking on the menu button. Select Extensions from the More Tools sub-menu.
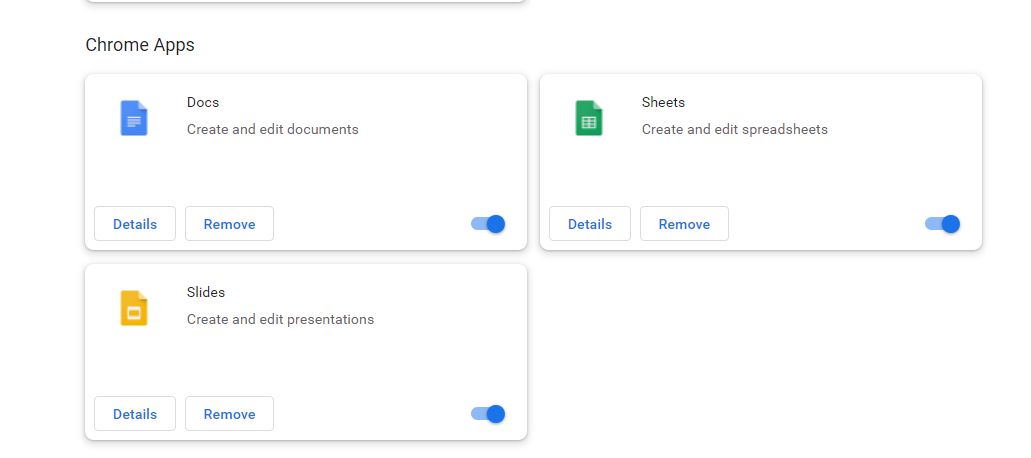
Step 2: A screen that lists all of the extensions you’ve installed on your Chrome browser will appear. To turn them off, click the toggle switch next to each one.
Step 3: After you’ve disabled all of the extensions, restart Chrome and see if you’re able to fix Your Connection is Not Private Error.
Step 4: If it does, one of the extensions is to blame for the issue. Turn them on one by one to discover the broken extension, and then uninstall it once you’ve found it.
Methods to Fix Server DNS Address Could Not Be Found Error
Method 1: Edit the Windows Host file
Step 1: Go to this PC> System32>Drivers or This PC>search etc.
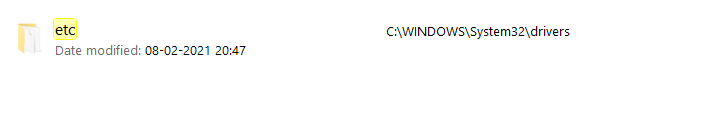
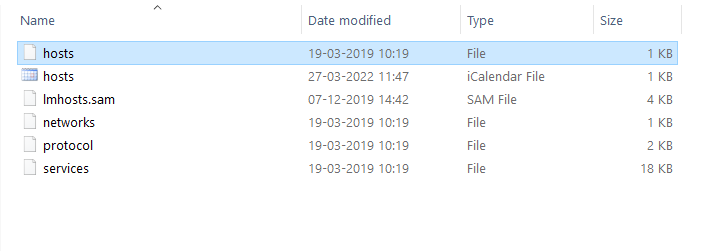
Step 2: Open the ‘hosts’ file. And select the notepad to read the file.
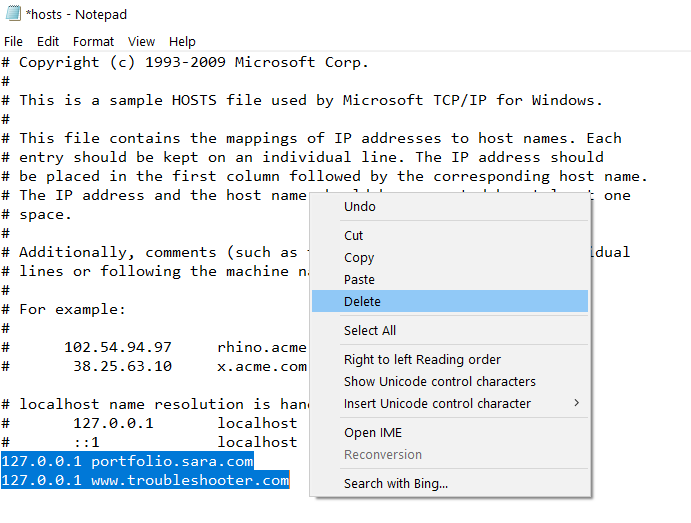
Step 3: Delete everything after the last # sign.
Method 2: Use a different DNS server
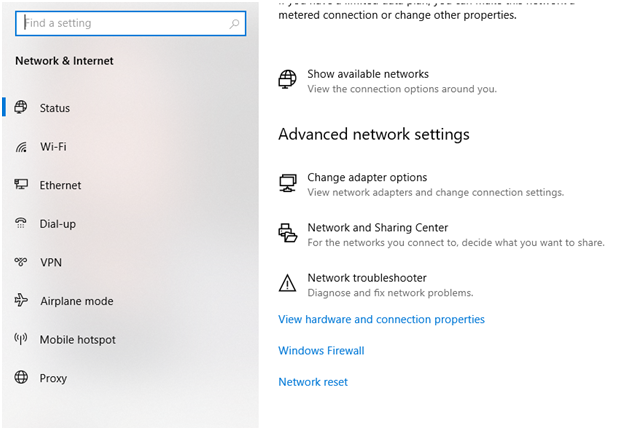
Step 1: To open the Network and Sharing Center, right-click on the Wi-Fi symbol in the system tray and select “Open Network and Sharing Center.”
Step 2: Select “Network and Sharing Center” from the drop-down menu.
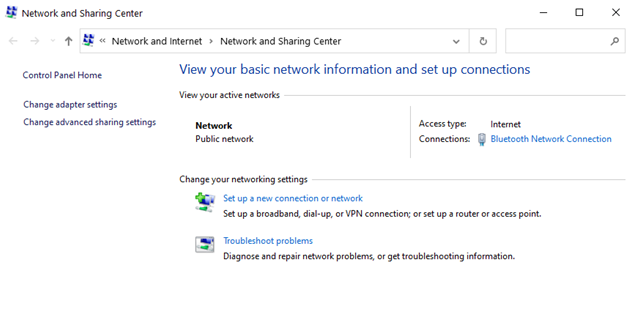
Step 3: Next, enter Settings and then Properties by clicking on your current connection.
Step 4: Next, go to Properties and pick “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IP)”.
Step 5: Next, pick “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IP)” and go to Properties.
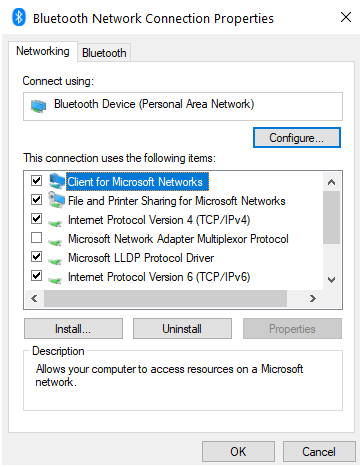
Step 6: Select “Use the following DNS server addresses” from the drop-down menu.
Step 7: In the Preferred DNS server and Alternate DNS server fields, type the following addresses:
8.8.8.8
8.8.4.4
You can also use other Public DNS Servers instead of Google DNS. Finally, to utilize Google DNS or OpenDNS, click the OK box.
Step 7: Select “Validate settings upon leaving” from the drop-down menu and click OK and Close.
Method 2: Reset Windows Socket Configuration
The Windows Socket Configuration (WinSock) is a set of parameters that the operating system uses to connect to the internet.
It is made up of socket program code that sends a request and receives a response from a remote server.
It is possible to reset all network configuration settings on a Windows PC using the netsh command.
Step 1: Open the Windows search by pressing Windows Key + S, then typing cmd or Command Prompt and selecting Run as Administrator.
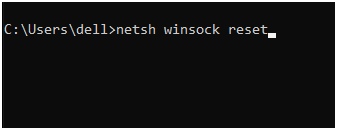
Step 2: Press Enter after typing the following commands:
netsh winsock reset
netsh int ip reset
Step 3: Restart your computer after the Windows Socket catalog has been reset to apply the modifications.
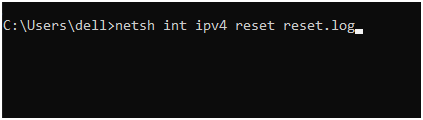
Step 4: Open the Command Prompt once more, then type and hit Enter to enter the following command:
netsh int ipv4 reset reset.log
Method 3: Flush the DNS Resolver Cache to Re-initialize DNS
The local DNS resolver cache can sometimes interfere with its cloud counterpart, making it harder to load new websites.
The online cache is prevented from storing new data on the computer by a local database of frequently resolved websites.
Clearing the DNS cache is required to resolve this issue.
Step 1: Open the Command Prompt as an administrator.
Step 2: Now run ipconfig /flushdns into the command prompt and hit Enter.

Step 3: If the DNS cache is successfully flushed, the following message will appear:
DNS Resolver cache was successfully fetched.
Step 4: Now restart your computer to see whether the Site Can’t Be Reached, Server IP Could Not Be Found problem has been resolved.
Method 4: Restart DNS client
Step 1: Click on the Windows icon or press the windows button, then search for services or press the Windows key plus R then type services.msc then press enter.
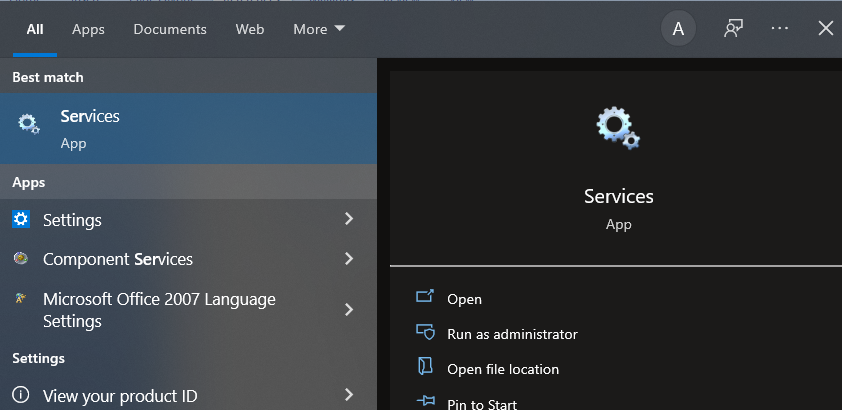
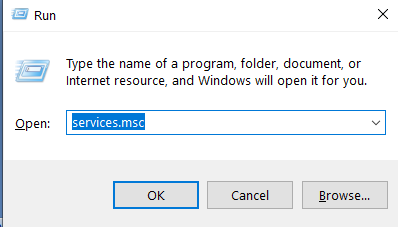
Step 2: Scroll down to “Network Store Interface Service” and click it (Press N to easily find it). Right-click Network Store Interface Service and choose Restart from the context menu.

Step 3: Repeat the above step in the services list for the DNS and DHCP clients.
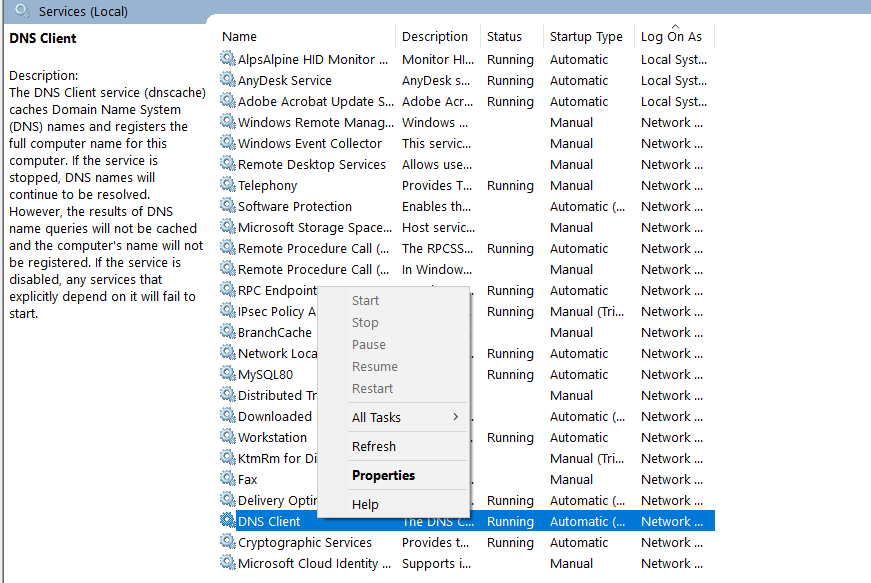
Step 4: Now that the DNS client has restarted, check to see if you were able to resolve the problem.
Method 5: Run Network Troubleshooter
Step 1: Press Windows + R and type ncpa.cpl and click on OK.
Step 2: Then click on diagnose.
Step 3: Allow the Network Troubleshooter to run, and the following error notice will appear:
“Wireless Network Connection” does not have DHCP enabled.
Step 4: Select “Try these Repairs as an Administrator” from the drop-down menu.
Step 5: Click Apply this Fix on the following prompt.
Method 6: Reset Chrome Browser
Note: Before continuing, make a backup of your Chrome data.
Step 1: Go to Chrome Settings, scroll down to Advanced, and click it.
Step 2: Go to the advanced tab. Click on “reset and cleanup.”
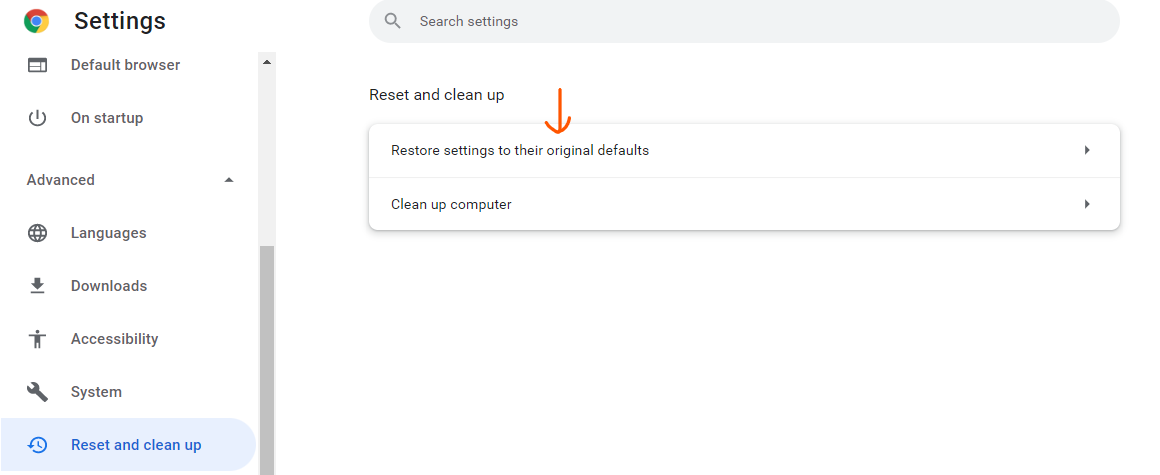
Step 3: When you’re sure you want to restore Chrome to its original settings, click the Reset settings option in the dialogue box below.
Method 7: Reinstall Chrome
Step 1: Access Settings by pressing Windows Key + I, then select Apps.
Step 2: Select “Apps & Features” from the left-hand menu.
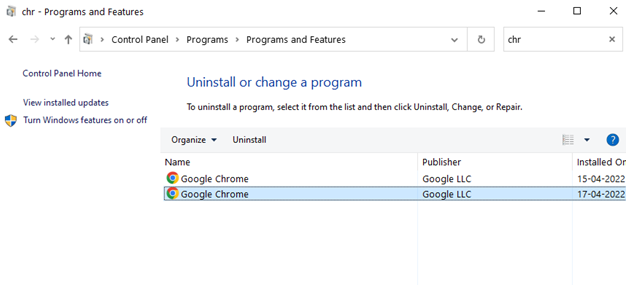
Step 3: Go to the bottom of the page and look for “Google Chrome.”
Step 4: Select Google Chrome and then the Uninstall option.
Step 5: Confirm Chrome’s deletion by clicking the Uninstall icon once more.
Step 6: Once Chrome has been uninstalled, restart your computer to apply the changes.
Step 7: Download and install the most recent version of Google Chrome once more.
Note: Reinstalling Chrome will wipe out all of your data, so create a backup of your bookmarks, passwords, and settings before proceeding.
Method 8: Use Chrome Cleanup Tool
Cleaning the cache data assists in troubleshooting enhances web page loading times, and boosts your computer’s efficiency. The cache can cause issues with the view if the browser does not load the site’s current version, even if the site has changed since the last visit.
The cache on your Android phone is a collection of tiny data files that your apps and web browser used to improve efficiency. On the other hand, cache files might become corrupted or overloaded, resulting in performance difficulties.
Although the cache does not need to be cleaned regularly, doing so can be beneficial.
The official Google Chrome Cleanup Tool assists in scanning and removing applications that may cause issues with Chrome, such as crashes, strange startup pages or toolbars, unwanted adverts that won’t go away, or generally altering your surfing experience.
Conclusion
Hopefully, you’ve successfully fixed the Server DNS address that could be found as an error in Google Chrome. If you have any more questions, please leave them in the comments below, and please share this page on social media to assist your friends in solving this issue.


Leave a Reply